Monday, Monday, 25, 2020 will be a federal holiday in the District of Columbia. This means the USPTO will be closed. This means that any action that would be due at the USPTO on May 25 will be timely if it is done by Tuesday, May 26, 2020.
Asymmetric bandwidth
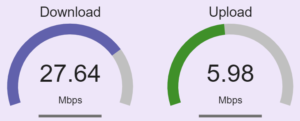
Before all of this work-from-home happened, I’d guess that most of us very very little thought to the extreme asymmetry in the internet service provided by our internet service providers. Continue reading “Asymmetric bandwidth”
What is a “UPRD application”?
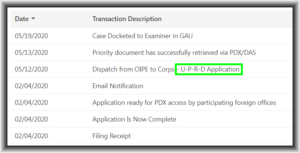
I was clicking around in Patentcenter (become a beta tester! — join the listserv!) and saw something that I had not seen before – a “Transaction Description” saying:
Dispatch from OIPE to Corps – U-P-R-D Application.
which prompted me to ask “what does ‘UPRD’ mean?”
USPTO clears two Patentcenter trouble tickets
Quite by accident today I stumbled upon the good news that USPTO fixed two bugs in Patentcenter, permitting us to clear two Patentcenter trouble tickets today. The cleared trouble tickets are:
- CP1 — Web-based Form 85B loses initial capitalization for assignee city name (see article)
- CP8 – Reel number displayed wrong (see article)
The trouble ticket page has been updated accordingly. This leaves twenty-one outstanding trouble tickets.
Of course what we can hope for is that eventually the Patentcenter developers will establish an outbound communications channel with the beta testing community, and will let us know when they fix a bug or add a requested feature. Until then, it will be a matter of our stumbling upon the fact of a bug having been fixed or a desirable feature having been added.
Spurious “user is not enrolled” error in Patentcenter
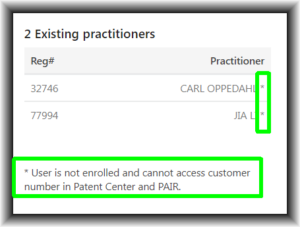
Patentcenter incorrectly lists every user as “not enrolled”. Patentcenter incorrectly says that every user “cannot access customer number in Patent Center and PAIR.”
To see this, log in at Patentcenter, click on “Manage”, click on “Manage customer numbers”. Then click on any customer number in your list. You will see that every user is flagged as being “not enrolled”.
This is bug report CP33.
“Update Application Address” is missing from Patentcenter
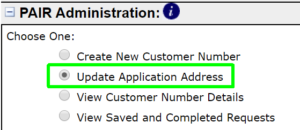
The “Update Application Address” function is an important part of Private PAIR. The corresponding function is missing from Patentcenter. This is feature request FR19.
EPO is still missing from Patentcenter Web-based ADS
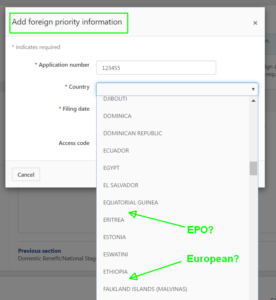
Six months have now passed since I first reported this problem to the EBC. Still it has not been fixed. EPO is missing from the Web-based ADS function in Patentcenter!
EPO is in the web-based ADS function in EFS-Web. But it is missing in the corresponding function in Patentcenter. This is bug report CP9 and you can read about it here.
This would be so very easy to fix. It would be a matter of adding one line of text in a list item on a web page.
Patentcenter Corrected ADS has gone missing
Without comment or explanation, the developers of Patentcenter have removed the Corrected ADS function from Patentcenter. In this April 30 blog article I reported that it was buggy. This became bug report CP4. Now it’s gone from Patentcenter.
Imminent: last 40 ack receipts in Patentcenter
When Patentcenter launched in alpha test in September of 2018, one of the first things that the alpha testers pointed out was that an important feature from EFS-Web was missing — the last 40 acknowledgment receipts. Continue reading “Imminent: last 40 ack receipts in Patentcenter”
How many 371 cases have been filed thus far in Patentcenter?
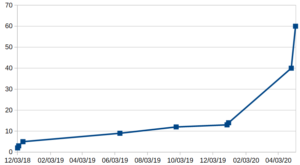
US national phase entries in Patentcenter are assigned from a block of application numbers starting at 15/733,001. Our firm was the third ever to file a 371 case in Patentcenter, receiving application number 15/733,003.
By the end of 2019, there had been fifteen 371 cases filed. My firm had filed seven of those cases. Yes my firm had done about half of all of the US national-phase work in Patentcenter from the beginnings of alpha test until the end of 2019.
By now, with Patentcenter opening up for general use, there has been an uptick in national-phase filings in Patentcenter. Twenty of them have been filed just in the past eight days.
